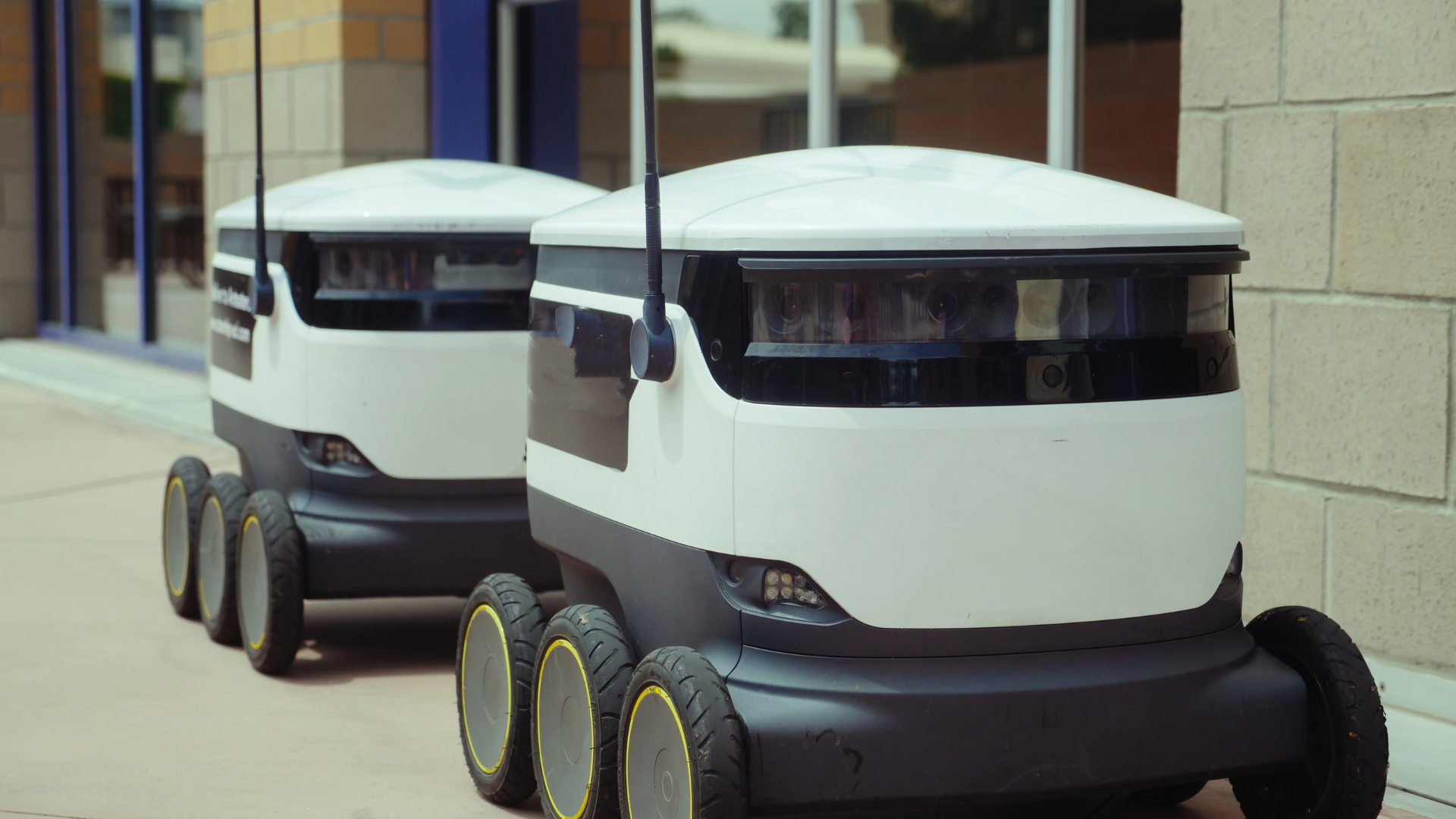
The rise of autonomous vehicles marks a pivotal moment for the transportation industry, with profound implications for how people and goods move. Autonomous vehicles will transform this sector by enhancing mobility, increasing efficiency, and reshaping urban landscapes. As self-driving technology progresses, it promises to alleviate traffic congestion and reduce emissions, making transportation more sustainable.
With the integration of these vehicles, companies are likely to see significant improvements in logistics and delivery systems. This shift not only streamlines operations but also allows for more flexible transport solutions tailored to specific needs. The transition to a more automated transport environment will redefine the very concept of commuting and goods transportation.
In addition to operational benefits, autonomous vehicles can enhance safety on the roads. With advanced sensors and real-time data processing, these vehicles are designed to minimise accidents and ensure a smoother travel experience. The future of transportation is poised for radical change, driven by the capabilities of autonomous driving technologies.
The Evolution of Autonomous Vehicle Technology
The evolution of autonomous vehicle technology hinges on significant advancements in artificial intelligence, enhancements in sensor capabilities, and the progression from advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) to full autonomy. These elements collectively contribute to the potential transformation of transportation.
Advancements in Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a pivotal role in the development of autonomous vehicles. Recent advancements in machine learning techniques enable systems to process vast amounts of data, allowing vehicles to make real-time decisions.
Neural networks, specifically deep learning models, are utilised for tasks such as object recognition and predictive analytics. This helps the vehicle understand its environment, predict the actions of other road users, and adjust its driving behaviour accordingly.
As AI continues to evolve, the potential for hands-free driving becomes increasingly viable. This progress is critical for achieving Level 4 and higher autonomy, where vehicles can operate independently in most scenarios.
The Role of Sensors and Computer Vision
Sensors and computer vision are integral to the functionality of autonomous vehicles. Various types of sensors, including Lidar, radar, and cameras, provide comprehensive data about the surroundings.
Lidar units create detailed 3D maps of the environment, while cameras offer visual recognition of road signs, pedestrians, and other vehicles. Radar complements these technologies by detecting motion and distance, especially in challenging weather conditions.
The integration of sensor data through advanced algorithms is what enables vehicles to perceive their environment accurately. Each sensor type brings unique advantages that support the vehicle’s decision-making processes, enhancing safety and reliability.
From ADAS to Full Autonomy
The journey from ADAS to full autonomy illustrates the gradual integration of automation in vehicles. Initially, systems like adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assist were introduced to enhance driving safety and comfort.
Level 3 automation allows for conditional driving automation, meaning the vehicle can handle most driving tasks but still requires human intervention in specific situations. Progressing to Level 4, vehicles can operate fully autonomously in certain environments without human input.
As technology continues to advance, the seamless transition from ADAS features to fully autonomous capabilities seems increasingly attainable. The focus now lies in software development and rigorous testing to ensure safety and performance standards are met.
Impact on Traffic Management and Road Safety
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) hold the potential to significantly influence traffic management and enhance road safety. By reducing human errors and optimising traffic flow, these vehicles can transform how roads operate.
Reducing Traffic Congestion
AVs can mitigate traffic congestion through improved routing and communication with traffic management systems. They are equipped with real-time data processing capabilities that enable them to assess traffic conditions faster than human drivers.
This efficiency allows AVs to adjust their routes dynamically based on traffic conditions. The ability to share information with other vehicles and infrastructure can lead to coordinated movements, reducing stop-and-go traffic. Less congestion results in shorter travel times and lower fuel consumption.
Improving Traffic Flow with AVs
The integration of AVs into existing traffic systems can improve overall traffic flow. These vehicles employ advanced algorithms that optimise speed, distance, and lane changes. By maintaining consistent speeds and safer following distances, AVs can enhance the smooth movement of traffic.
Additionally, automatic emergency braking systems in AVs can detect potential hazards and react faster than humans. This capability encourages smoother merges and less abrupt stops, which can further enhance traffic flow. By facilitating better interactions among vehicles, AVs can create a more harmonious driving environment.
Enhanced Road Safety
Road safety stands to benefit greatly from the deployment of autonomous vehicles. Human error is a significant factor in the majority of traffic accidents. AVs are designed to minimise these errors through various safety features.
With technologies such as automatic emergency braking and lane-keeping assistance, AVs can respond instantly to prevent collisions. Data from AVs can also help identify hazardous road conditions, enabling preemptive measures to enhance safety. The collective impact of these systems can lead to a noticeable decrease in accidents and fatalities on the roads.
However, even with advanced safety features and improved traffic management, accidents involving autonomous vehicles can still take place due to system failures, software glitches, or unexpected road conditions. When such incidents occur, determining liability can be complex, as multiple parties, such as vehicle manufacturers, software developers, or human supervisors, may be involved. In these situations, seeking guidance from an experienced personal injury lawyer becomes essential. A legal professional can help victims navigate the intricate claims process, protect their rights, and secure the compensation they deserve, including support to help with medical bills after an accident, lost income, and pain and suffering.
This complexity is particularly pronounced in accidents involving commercial vehicles. Bus accidents, for example, whether with human drivers or future autonomous systems, often involve intricate investigations due to federal and state regulations, multiple potential responsible parties, and the likelihood of severe injuries. Victims of such incidents, especially those occurring in specific jurisdictions, require specialized legal assistance to navigate the unique challenges. Understanding your rights and the nuances of pursuing bus crash injury claims in Alabama can be critical for securing fair compensation for medical expenses, lost wages, and other damages. This specialized focus ensures that all aspects of the claim, from liability to long-term care needs, are thoroughly addressed.
Advantages for the Transportation Sector
The introduction of autonomous vehicles is set to bring significant advantages to the transportation sector. Key areas of impact include enhancements in logistics efficiency, improved fuel sustainability, and the emergence of new business models that could reshape profitability.
Logistics and Last-Mile Delivery
Autonomous vehicles can optimise logistics by streamlining the supply chain. They offer increased precision in navigation and scheduling, reducing delivery times. These vehicles can operate continuously, thus increasing throughput.
Continuous operation raises practical maintenance needs for commercial fleets, where exterior and undercarriage grime can accelerate wear and even affect aerodynamics and fuel economy. Regular, environmentally conscious cleaning helps preserve vehicle condition and uptime without introducing harsh chemicals into the local watershed. For Edmonton operators balancing high utilization with sustainability goals, targeted services like Edmonton fleet washing can extend asset life and support compliance with municipal environmental standards. Integrating scheduled cleaning into fleet management complements the efficiency gains of automation by reducing unscheduled downtime.
Beyond preventative measures like cleaning, the demanding nature of commercial transport means that mechanical issues are inevitable. Heavy-duty vehicles, whether autonomous or human-driven, require specialized attention for complex systems like engines, transmissions, and brakes. When these critical components fail, prompt and expert Edmonton truck repairs are essential to minimize costly downtime and ensure operational continuity. Local specialists offer comprehensive diagnostics, routine maintenance, and emergency services, keeping fleets running efficiently and safely on Alberta’s roads. This proactive approach to maintenance and repair is crucial for maximizing the lifespan and reliability of any commercial fleet.
In last-mile delivery, autonomous vans and drones can access areas that may be difficult for traditional vehicles. This flexibility can lower costs for companies, leading to lower prices for consumers. As a result, businesses may gain a competitive advantage by improving service levels without sacrificing quality.
Fuel Efficiency and Sustainability
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to enhance fuel efficiency significantly. Advanced algorithms can optimise routes, reducing unnecessary mileage and fuel consumption. This efficiency can lead to lower operational costs and less wear on vehicles.
The sustainability impact is notable, as self-driving technology can contribute to a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions. With electric autonomous vehicles, the transportation sector can move towards greener alternatives. This shift supports public and corporate sustainability goals, promoting a positive image in the market.
Novel Business Models and Profitability
The rise of autonomous vehicles is paving the way for innovative business models. Subscription models for mobility services and robotaxis offer consumers flexibility and reduced reliance on car ownership. This model can lead to increased utilisation rates and potentially higher margins for service providers.
Autonomous trucking can transform freight logistics by reducing labour costs and increasing delivery capacity. As companies integrate these vehicles, they could see improved profitability from operational efficiencies. Embracing these changes will be crucial for businesses aiming to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Challenges and Considerations for the Future
As autonomous vehicles (AVs) become more prevalent, various challenges require attention. These include regulatory compliance, the need for substantial investments in infrastructure, and the transition towards an autonomous lifestyle.
Regulatory Compliance and Public Trust
Navigating the regulatory landscape is critical for the deployment of AVs. Governments need to create clear guidelines that ensure safety while fostering innovation. Regulatory bodies must also address liability concerns regarding accidents involving AVs.
Public trust remains vital for the acceptance of this technology. Engaging the community through transparent communication about safety measures and operational protocols can help build confidence. Companies like Waymo and Tesla actively participate in public awareness initiatives to enhance understanding.
Investment and Infrastructure Development
Significant funding is necessary to transform the current infrastructure into one that supports AVs. Urban areas will require updates to roadways, signage, and traffic management systems to accommodate these vehicles. Predictive maintenance technologies will also need to be integrated into existing systems.
Investors play a crucial role in this transformation. By funding research and development, companies can accelerate innovations in fleet management and operational efficiency. Partnerships between the public and private sectors will be essential to secure the required capital for infrastructure investments.
Towards an Autonomous Lifestyle
Transitioning towards an autonomous lifestyle involves changes in how society perceives transportation. AVs could reshape urban environments by reducing congestion and increasing road safety. This shift necessitates adapting urban design to incorporate dedicated lanes and hubs for AV operations.
Consumer behaviour may also change as reliance on personal vehicles diminishes. The convenience of shared AVs could lead to decreased car ownership and a shift towards sustainable transport solutions. For industry leaders, understanding these behavioural shifts will be crucial for developing effective business models.